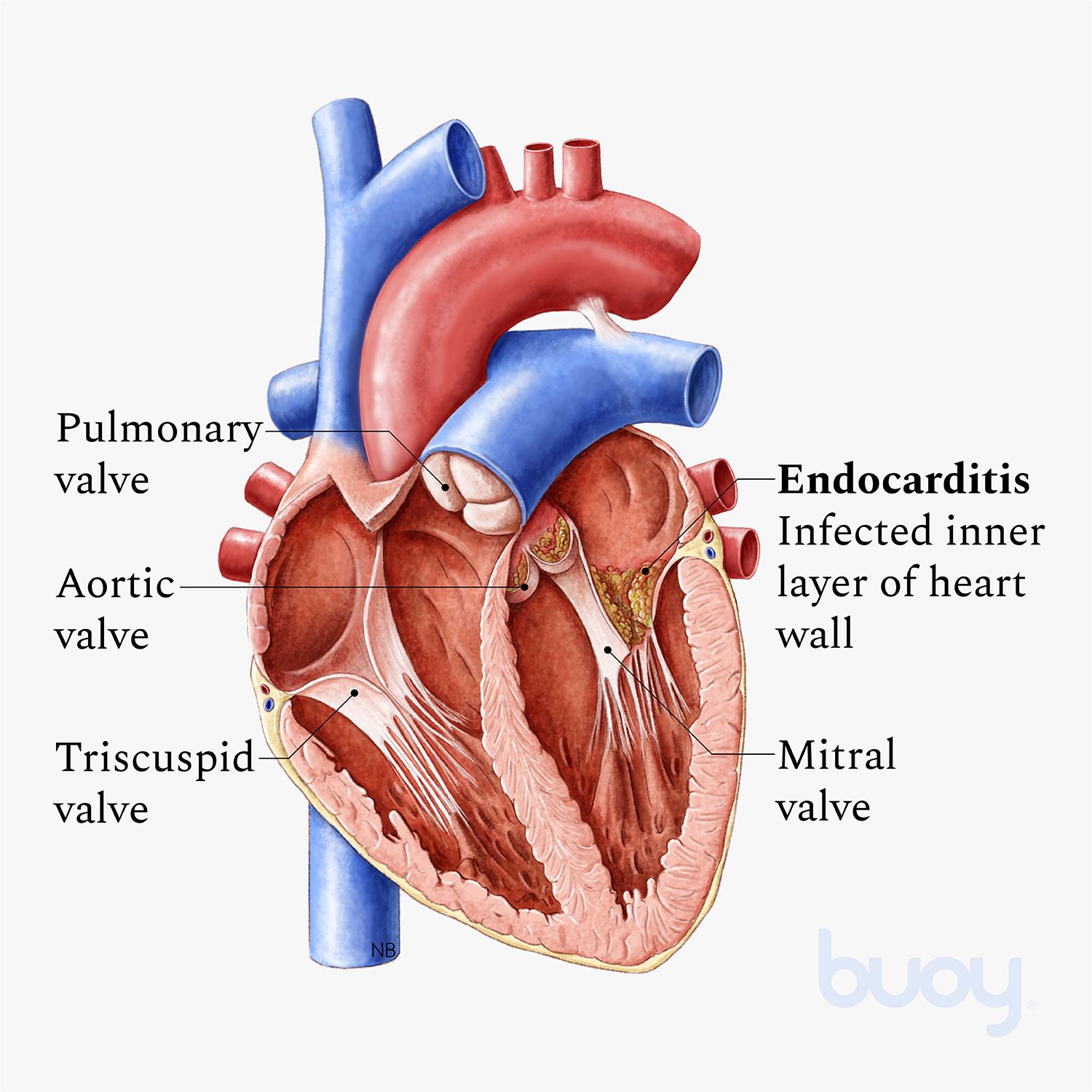
Infective endocarditis is an infection of the lining of the heart's chambers or the heart's valves. If left untreated, endocarditis can cause other complications, such as a blood clot, an irregular heartbeat, valve damage or destruction, and, in time, congestive heart failure (CHF).
Endocarditis generally occurs when bacteria or other germs from another part of your body, such as your mouth, spread through your bloodstream and attach to damaged areas in your heart.
Endocarditis may develop slowly or suddenly - depending on what's causing the infection and whether you have any underlying heart problems. Endocarditis signs and symptoms vary, but may include:
- Fever and chills
- A new or changed heart murmur - heart sounds made by blood rushing through your heart
- Fatigue
- Aching joints and muscles
- Night sweats
- Shortness of breath
- Paleness
- Unexplained weight loss
Various tests may be necessary to help make the diagnosis:
- Blood tests
- Transesophageal echocardiogram
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Chest X-ray
- Computerized tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
The first line of treatment for endocarditis is antibiotics.
If you have endocarditis, you may need high doses of intravenous (IV) antibiotics in the hospital.
Surgery is also sometimes needed to treat endocarditis that's caused by a fungal infection.
BestHeartSurgery is a comprehensive information portal that gives both the common man and medical professionals.

