Congenital heart procedures are surgeries or interventions performed to correct heart defects present at birth. These defects, known as congenital heart defects, can range from simple issues like holes in the heart (septal defects) to more complex malformations that affect the heart's structure and function. Congenital heart procedures are designed to restore normal blood flow, improve heart function, and enhance the quality of life for affected individuals. Depending on the severity of the defect, treatment options may include open-heart surgery, minimally invasive catheter-based procedures, or hybrid approaches. Advances in medical technology and surgical techniques have significantly improved outcomes, allowing many patients to lead healthy, active lives post-surgery.
Congenital heart disease can describe a number of different problems affecting the heart. It is the most common type of birth defect. CHD causes more deaths in the first year of life than any other birth defects.
Congenital heart disease is often divided into 2 types: cyanotic (blue skin color caused by a lack of oxygen) and non-cyanotic. The following lists cover the most common congenital heart diseases:
Cyanotic:
- Ebstein's anomaly
- Hypoplastic left heart
- Pulmonary atresia
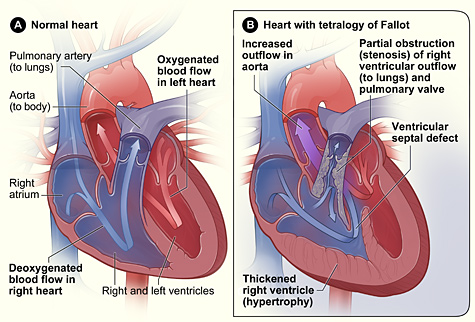
- Tetralogy of Fallot
- Total anomalous pulmonary venous return
- Transposition of the great vessels
- Tricuspid atresia
- Truncus arteriosus
Non-cyanotic:
- Aortic stenosis
- Atrial septal defect (ASD)
- Atrioventricular canal (endocardial cushion defect)
- Coarctation of the aorta
- Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
- Pulmonic stenosis
- Ventricular septal defect (VSD)


BestHeartSurgery is a comprehensive information portal that gives both the common man and medical professionals.

